Radiography is a technique that uses radiation to produce images of objects that are not visible to the naked eye. This method has been widely used in both medical and industrial fields for decades. In the medical field, radiography helps doctors visualize internal structures such as bones, tissues, and organs, allowing them to diagnose and treat various conditions effectively. In industry, radiography serves a similar but more specialized purpose. It enables inspectors to detect hidden flaws or defects in materials and equipment that could compromise their integrity or safety. This makes it an essential tool in quality control and maintenance across many sectors. This guide will explore the applications of industrial radiography in different industries, focusing on how it supports inspection processes. If you're interested in learning about its use in healthcare, we recommend checking out this informative article from the FDA. [Industrial radiography is one of several non-destructive testing (NDT) methods used by professionals to evaluate materials without damaging them. Learn more about NDT in this detailed guide.] [Note: Industrial radiography is sometimes referred to as industrial radiology.] Industrial radiography (IR) involves using radiation—such as gamma rays or x-rays—to examine the internal structure of materials and components. This technique allows inspectors to identify potential issues without altering or destroying the object being tested. Both gamma rays and x-rays are commonly used in industrial radiography. These types of radiation can penetrate through various materials, enabling non-invasive inspections. This makes it ideal for assessing the quality and integrity of parts and systems in a wide range of industries. The two main applications of industrial radiography are: Manufacturers use it to detect internal defects in raw materials or finished products before they reach the market. Inspectors use it to evaluate the condition of industrial assets, ensuring they meet safety and compliance standards. Industries like automotive and aerospace frequently use radiography to inspect critical components. In manufacturing, it helps ensure that parts are free from cracks, voids, or other imperfections that could lead to failure. [Related read: What Is a Dosimeter and Why Is It Important?] Other sectors, such as oil and gas, power generation, and construction, rely on radiography during inspections of pipelines, welds, and pressure vessels. These industries depend on regular checks to prevent accidents and maintain operational efficiency. One key advantage of industrial radiography is that it's a non-destructive testing (NDT) method. This means that the material being inspected remains intact after the process. Unlike destructive testing, which may require cutting, breaking, or otherwise altering the sample, NDT preserves the object’s original state. Destructive testing, on the other hand, involves removing samples or modifying the material to analyze its properties. For example, chemical tests on paint to detect lead would permanently alter the surface, making it unsuitable for further use. Non-destructive methods like radiography are preferred when the goal is to assess quality without compromising the integrity of the asset. Industrial radiography involves the use of radiation, which can be harmful if not handled properly. The sources of radiation can include machines or radioactive materials, and exposure to these can pose serious health risks. It’s important to note that industrial radiographers face some of the highest risks among workers who handle radiation. That’s why strict safety protocols and regulations are in place to protect both workers and the public. Compliance with these rules is mandatory, and training, licensing, and proper equipment are all part of the process. You can find more information about safety requirements in the Careers and Salary section below. Radiographic testing is a method where radiation is used to inspect the internal structure of a material. The process typically involves the following steps: Position the radiation source. An inspector directs either gamma rays or x-rays toward the object being tested. Place the detector. A detector is positioned on the opposite side of the object to capture the radiation that passes through it. Capture the image. The detector records the intensity of radiation that reaches it, creating a visual representation of the object’s internal structure. Analyze the results. Inspectors review the images to identify any anomalies, such as cracks, voids, or inconsistencies in material thickness. The images produced are known as radiographs. While traditional film was once the standard, modern systems now primarily use digital technology for faster and more accurate analysis. By analyzing the variation in radiation absorption, inspectors can determine the condition of the material. Areas where less radiation passes through indicate thicker sections, while areas with more radiation suggest thinner or damaged regions. Industrial radiography relies on two main types of equipment: those that use x-rays and those that use gamma rays. Each has its own advantages and limitations depending on the application. Gamma ray-based equipment uses radiation emitted from radioactive sources contained within the device. This type of system is compact and portable, making it suitable for use in tight spaces. However, unlike x-ray machines, gamma ray equipment cannot be turned off. This means it continuously emits radiation, and the only way to protect workers is by enclosing the device in a shielded container. X-ray equipment is typically larger and requires a power source. It can be turned on and off, making it safer to use in environments where workers are present. Because of the potential hazards associated with radiation, the use, ownership, and transportation of radiography equipment are strictly regulated. In the U.S., the Nuclear Regulatory Commission oversees these activities and sets licensing requirements. For more details on regulations, visit the official NRC website. If you’re considering a career in industrial radiography, here are the basic requirements to get started: A high school diploma or equivalent A certificate from an accredited industrial radiography training program An industrial radiographer is a professional who uses radiation to inspect materials, equipment, and structures for signs of damage or defects. They play a crucial role in ensuring the safety and reliability of critical infrastructure. These professionals often work with large, stationary assets such as pipelines, boilers, and welding joints. Their job involves setting up the imaging equipment, capturing the data, and analyzing the resulting images for any irregularities. Alongside technical skills, industrial radiographers must also follow strict safety protocols to minimize their exposure to radiation. This includes wearing protective gear and adhering to established procedures. Most jobs in this field are full-time and involve traveling to various job sites. Since the objects being inspected are usually large and fixed in place, radiographers often have to go to the location rather than bringing the equipment to a central facility. According to ZipRecruiter, the average annual salary for an industrial radiographer in the U.S. is around $54,000. However, this figure can vary significantly based on factors such as experience, location, and additional certifications. Some of the top-paying positions are found in states with high demand for skilled inspectors, particularly in industries like energy and manufacturing. Obtaining additional certifications, such as those related to specific types of equipment or advanced imaging techniques, can also increase earning potential and open up new opportunities in the field. Certification is required in most jurisdictions to legally perform industrial radiography. The process typically includes hands-on training, radiation safety education, and passing a written exam. Common certifications include: RAM: Certification for working with radioactive materials. X-RAY: Certification for operating x-ray equipment. Both: Certification for both radioactive materials and x-ray machines. Each state may have its own specific requirements, so it's best to check with local regulatory bodies for the most up-to-date information. As technology continues to evolve, we may soon see more advanced imaging techniques, including 3D modeling, that could enhance the accuracy and efficiency of industrial radiography. While drones are not yet widely used in industrial radiography, they are beginning to make an impact in certain specialized applications. One notable example is the DroneX, developed by Pacific Imaging. The DroneX is equipped with an x-ray imaging system and is used to inspect conductor sleeves on power lines. This innovation allows inspectors to gather data without the need for manual access, reducing risk and increasing efficiency. This drone has already been deployed for power line inspections, offering a safer and more efficient alternative to traditional manual methods. As drone technology advances, we may see more applications of this kind, expanding the possibilities of industrial radiography in the future. The inflatable arch sprinkler, children can pass through the curtains, play in the backyard, courtyard and lawn, bringing a lot of summer fun in the hot weather. The inflatable sprinkler is made of high -quality thick PVC materials, which is durable to prevent holes or puncture. arch sprinkler, inflatable sprinkler arch, arch sprinkler toys, arch water sprinkler, inflatable water arch sprinkler Lixin Outdoor Product Co., Ltd , https://www.pdinflatable.comWhat Is Industrial Radiography Used For?
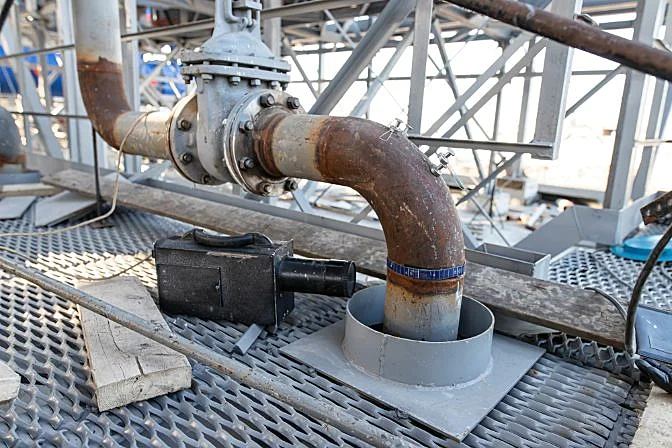 Radiographic testing used on a pipe
Radiographic testing used on a pipeIndustrial Radiography
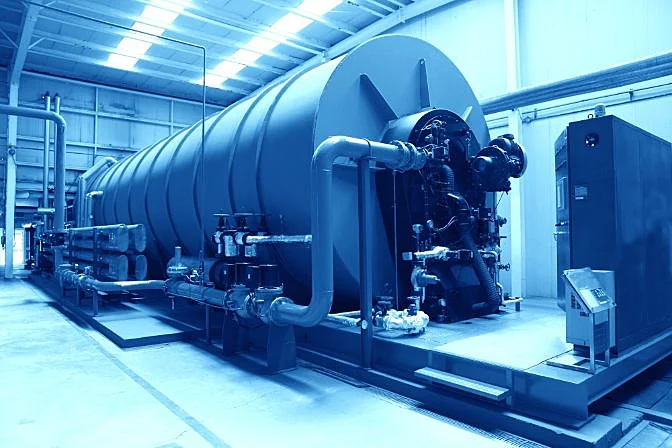 An industrial boiler
An industrial boilerNon-Destructive vs. Destructive Testing
A Note on Safety in Industrial Radiography
Radiographic Testing—How Does It Work?
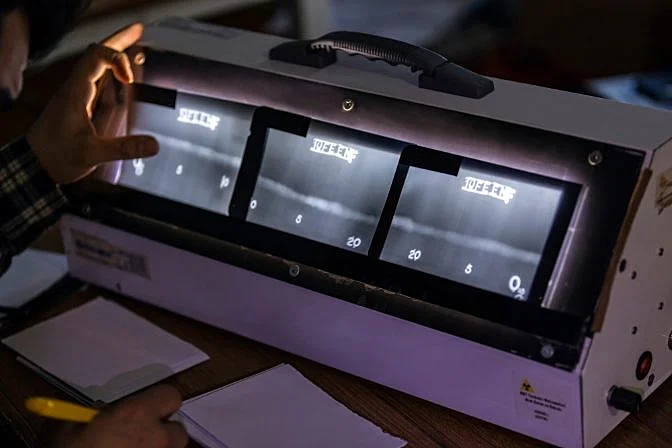

Industrial Radiography Equipment
Gamma Rays Industrial Uses & Equipment
X-Rays Industrial Uses & Equipment
Industrial Radiographer Salary and Careers
What Is an Industrial Radiographer?
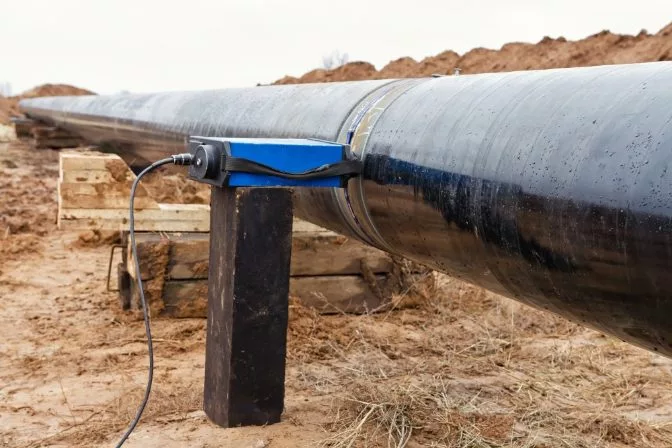 Radiographic testing used on a weld in an aboveground pipe
Radiographic testing used on a weld in an aboveground pipeWhat Does an Industrial Radiographer Salary Look Like?
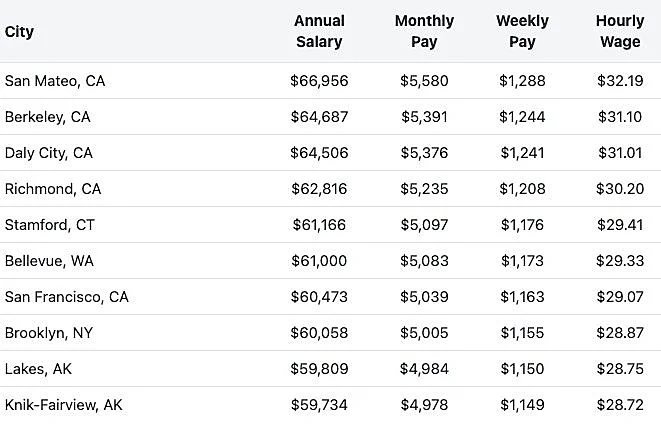 Data provided by ZipRecruiter
Data provided by ZipRecruiterIndustrial Radiography Certification
Drones and Industrial Radiography
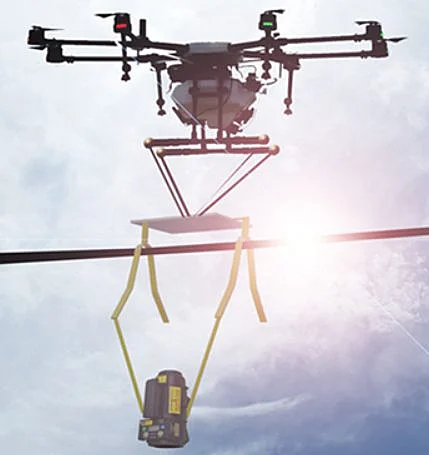 Photo credit: Pacific Imaging
Photo credit: Pacific Imaging
The Inflatable Sprinkler Items is easy to use. It needs to be inflated with a gas pump to the sprinkler (excluding), connect it to any garden hose, and then fill the base with water to help it stand stably. Dowry smoothly in the holes. By the way, if it is flipped or over, the water in the base must be full.
The inflatable sprinkler is not only suitable for summer outdoor sprayed toys for children, boys and girls, but also very suitable for children's swimming pools, beach lawn and children's birthday party. Any interesting parents can run with their children under the sprinkler, for a few hours, bringing a lot of fun in hot summer weather.
What Is Industrial Radiography Used For?