Radiography is a technique that uses radiation to create images of objects or structures that are not visible to the naked eye. It's a powerful tool for inspecting materials and identifying internal issues without damaging the object being tested. In the medical field, radiography is widely used to visualize internal body structures such as bones, tissues, and organs. This helps doctors diagnose conditions and plan treatments effectively. Similarly, in industrial settings, radiography plays a crucial role in detecting hidden flaws or defects within materials and equipment. It allows inspectors to ensure the structural integrity and safety of critical components without having to disassemble them. This guide will explore the various applications of industrial radiography across different industries, focusing on how it supports inspection processes. If you're interested in how radiography is used in medical contexts, we recommend checking out the FDA's resources. [Industrial radiography is one of many non-destructive testing (NDT) methods used by inspectors. Learn more about NDT in this comprehensive guide.] [Note: Industrial radiography is also sometimes referred to as industrial radiology.] Industrial radiography (IR) is the process of using radiation—such as gamma rays or x-rays—to examine the internal structure of materials or components. It’s an essential method for quality control and safety assessments in various industries. Both gamma rays and x-rays are commonly used in industrial radiography. These forms of radiation can penetrate through many materials, enabling inspectors to detect internal flaws, cracks, or inconsistencies without altering the object itself. Industrial radiography has two main applications: Manufacturers use it to identify defects in raw materials or finished products before they reach the market. Inspectors use it to evaluate the condition of industrial assets, ensuring they meet safety and regulatory standards. Industries like automotive and aerospace frequently rely on radiographic testing to check the quality of vehicle parts and aircraft components. Similarly, sectors such as oil and gas, power generation, and construction use it to inspect pipelines, welds, and boilers. [Related read: What Is a Dosimeter and Why Is It Important?] One of the key advantages of industrial radiography is that it’s a non-destructive testing (NDT) method. This means that the material being tested remains intact and undamaged during the process. In contrast, destructive testing involves altering or sampling the material to analyze its properties. For example, chemical tests on paint to detect lead would permanently change the sample, making it unsuitable for further use. While industrial radiography is a highly effective inspection method, it involves the use of ionizing radiation, which can be harmful if not handled properly. Radiographers must follow strict safety protocols to protect themselves and others from unnecessary exposure. According to industry reports, accidents involving radiation are more common in industrial radiography than in other radiation-related jobs. This is why strict regulations and licensing requirements are in place for those who work with radiography equipment. For more information on safety procedures, see the Careers and Salary section below. Radiographic testing involves directing radiation through an object and capturing the resulting image on a detector. This process allows inspectors to identify internal defects or irregularities. The basic steps involved in radiographic testing include: Positioning the radiation source: An inspector directs gamma rays or x-rays at the object under inspection. Placing the detector: A detector is positioned on the opposite side of the object to capture the radiation that passes through it. Recording the data: The detector records the intensity of radiation passing through the object. Analyzing the results: The recorded data is analyzed to determine the internal condition of the object. The key benefit of this method lies in its ability to reveal internal structures without physical contact or damage. By analyzing the variations in radiation absorption, inspectors can spot potential flaws such as cracks, voids, or weak spots in materials. The images produced by radiographic testing are called radiographs. While traditional film was once used, modern systems now rely on digital imaging for faster and more accurate analysis. Industrial radiography relies on two primary types of radiation: x-rays and gamma rays. Each type of radiation has specific applications and equipment associated with it. Gamma ray equipment uses radioactive sources contained within the device. These systems are compact and portable, making them ideal for use in confined spaces. However, unlike x-ray machines, gamma ray devices cannot be turned off, meaning they emit radiation continuously. To protect workers, gamma ray equipment must be enclosed in a shielded housing. This ensures that radiation exposure is minimized during operations. X-ray equipment is typically larger and requires a power source. Unlike gamma ray systems, x-ray machines can be turned on and off, making them safer to handle when not in use. Due to the potential risks associated with radiation, the ownership, use, and transportation of radiography equipment require proper licensing in many countries, including the United States. In the U.S., the Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) oversees these regulations. If you're considering a career in industrial radiography, here’s what you need to know: A high school diploma or equivalent A certificate from a recognized industrial radiographer training program An industrial radiographer uses radiation to inspect materials, equipment, and structures for internal flaws. They create images using x-rays and analyze them to detect cracks, voids, or other imperfections that could compromise safety or performance. These professionals often work on large, stationary assets such as pipelines, pressure vessels, and welds. Their inspections are critical in industries like oil and gas, power generation, and manufacturing. Throughout their work, industrial radiographers must follow strict safety protocols to minimize radiation exposure. Jobs in this field are typically full-time, and professionals often travel to job sites where the equipment being inspected is located. According to ZipRecruiter, the national average salary for an industrial radiographer in the U.S. is approximately $54,000 per year. Salaries can vary significantly based on location, experience, and additional certifications. Obtaining additional certifications, such as those related to radiation safety or advanced inspection techniques, can significantly increase earning potential and open up new career opportunities. In the U.S. and other countries, industrial radiographers must be certified to perform their duties. Certification typically includes hands-on training, radiation safety education, and passing a written exam. Common certifications include: RAM – Certification for handling radioactive materials X-RAY – Certification for operating x-ray equipment Combined – Certification for both radioactive materials and x-ray machines Many states have their own certification programs, and some are nationally recognized. For more details, visit official regulatory websites. Although drones are not yet widely used in industrial radiography, their integration into the field is an emerging trend. One example is the DroneX system developed by Pacific Imaging, which is equipped with an x-ray imaging unit. The DroneX is used to inspect conductor sleeves on power lines, reducing the need for manual inspections that involve climbing or working at heights. This technology enhances safety while improving efficiency in infrastructure maintenance. As drone technology continues to evolve, we may see more innovations in how radiography is applied in the field. Drones equipped with x-ray imaging could revolutionize how inspections are conducted, especially in hard-to-reach or hazardous environments. Children's Inflatable Toys refer to toys made by using the tension force of the film material and the air pressure difference between the inside and outside of the film. The storage volume after it is released is small, and it is easy to carry and store. Great for children to play with, keep the gas in the shape that children like, and because of the light nature of the gas, it won't hurt to hit a child.
Small children's toys are soft, elastic and cute, Inflatable Toss Target Toy is safe and exciting, interesting and can stimulate children's competitiveness, and water inflatable toys are very fun.
outdoor inflatable toys for kids, inflatable toss target toy, inflatable ring toss game sets, inflatable kids toys, inflatable game Lixin Outdoor Product Co., Ltd , https://www.pdinflatable.comWhat Is Industrial Radiography Used For?
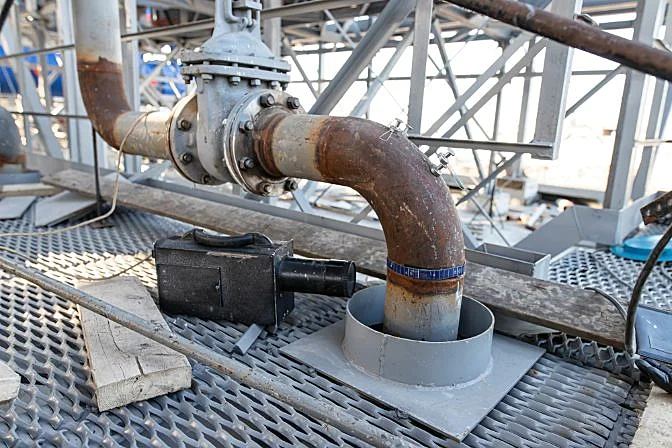 Radiographic testing used on a pipe
Radiographic testing used on a pipeWhat Is Industrial Radiography?
Non-Destructive vs. Destructive Testing
Safety Considerations in Industrial Radiography
How Does Radiographic Testing Work?
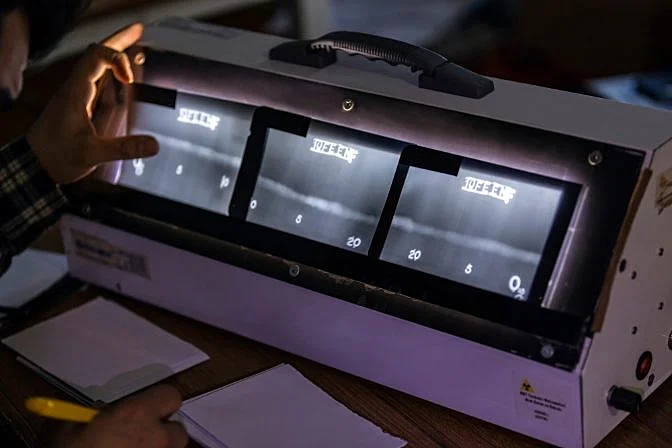

Industrial Radiography Equipment
Gamma Ray Radiography
X-Ray Radiography
Careers in Industrial Radiography
What Does an Industrial Radiographer Do?
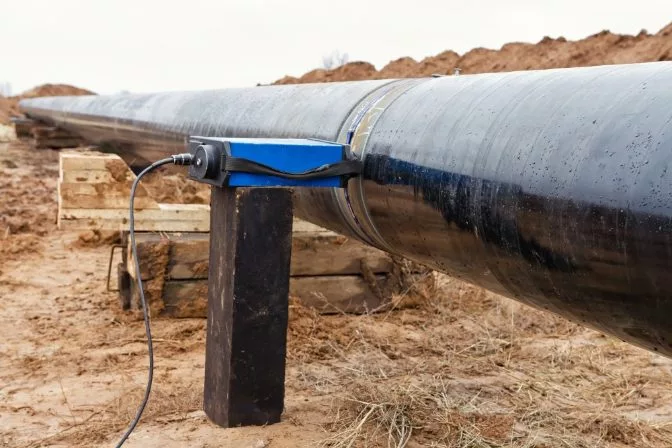 Radiographic testing used on a weld in an aboveground pipe
Radiographic testing used on a weld in an aboveground pipeSalary Overview
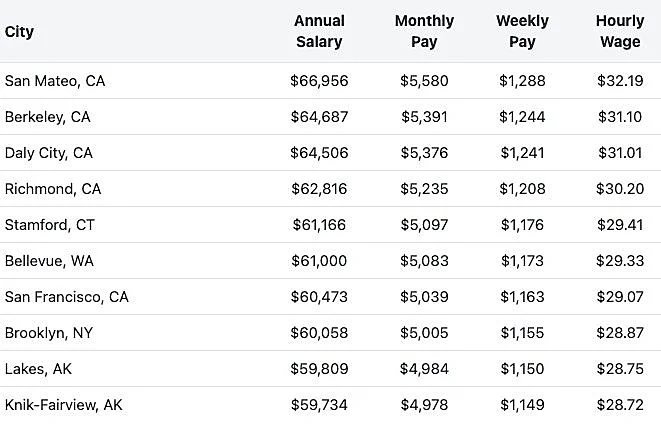 Data provided by ZipRecruiter
Data provided by ZipRecruiterCertification Requirements
Drones and Industrial Radiography
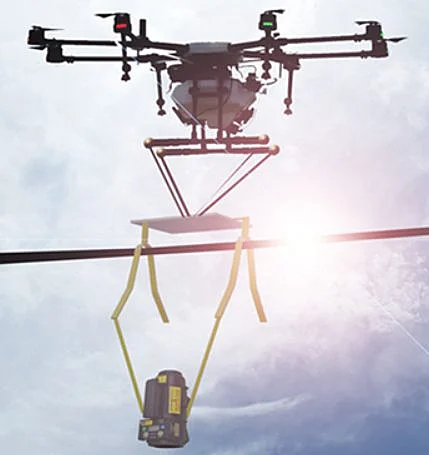 Photo credit: Pacific Imaging
Photo credit: Pacific Imaging
What Is Industrial Radiography Used For?