CCDs consist of many photosensitive units, usually in megapixel units. When the CCD surface is exposed to light, each photosensitive unit will reflect the charge on the component, and the signals generated by all the photosensitive units are added together to form a complete picture.
The more prominent features of CCD are:
1. Mature technology
2. High imaging quality
3 high sensitivity, low noise, large dynamic range
4. Fast response, self-scanning function, small image distortion, no afterimage
5. Application of VLSI process technology, high pixel integration, precise dimensions
There are many indicators to evaluate the quality of a CCD sensor, such as the number of pixels, CCD size, signal to noise ratio, and so on. The number of pixels and the size of the CCD are the most important indicators. The number of pixels refers to the number of photosensitive elements on the CCD.
We can think of the picture we have captured as consisting of many small points, each of which is a pixel. Obviously, the greater the number of pixels, the clearer the picture will be. If the CCD does not have enough pixels, the sharpness of the captured picture will be greatly affected.
Therefore, the CCD should have as many pixels as possible. However, increasing the number of pixels in a CCD in order to obtain better image quality will inevitably lead to a problem that is the increase in the cost of CCD manufacturing and the decrease in yield.
Therefore, for a series of problems such as cost, a lower-cost, lower-power, and highly-integrated CMOS sensor emerged.
CMOS is an important chip in the computer system, which saves the most basic information of the system.
The manufacturing technology of CMOS is no different from that of a general computer chip. It is mainly a semiconductor made of silicon and germanium, which makes it possible to coexist a negatively charged N-pole and a positively charged P-polar semiconductor on CMOS. The current generated by the two positive and negative complementary effects can be recorded and converted into images by the processing chip. Later, it was found that CMOS can also be used as an image sensor in digital photography.
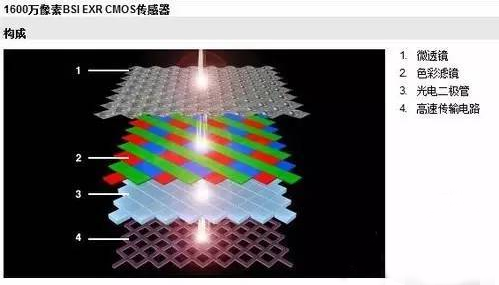
CMOS image sensor is a typical solid-state imaging sensor and has a common historical origin with CCD. CMOS image sensors are usually composed of elements such as sensitive cell arrays, row drivers, column drivers, timing control logic, AD converters, data bus output interfaces, and control interfaces. These parts are usually integrated on the same silicon chip. The working process can generally be divided into reset, photoelectric conversion, integration, read out several parts.
The photoelectric information conversion function of CMOS is basically similar to that of the CCD. The difference lies in the difference in the information transmission mode after the photoelectric conversion between the two sensors.
CMOS composition
CMOS has the advantages of simple information reading method, fast output information rate, low power consumption (only about 1/10 of the CCD chip), small size, light weight, high integration, and low price.
It is to take into account that the CMOS sensor's production cost and yield are higher than the CCD sensor, so several well-known manufacturers since the 2000 began to increase the CMOS sensor research and development work, the current CMOS growth rate has reached several times At the CCD level.
We can see that even in the early days of Nikon’s digital SLR products, there were some models of cameras that use CCD sensors. However, whether Nikon, Sony, or Canon’s digital cameras have been introduced in recent years, we’re basically hard. See CCD traces again.
Although the use of CMOS sensors will save the camera's cost, the image quality is still the most important for the camera. CMOS is the most fatal injury compared to the CCD is the quality, because of the obvious shortcomings of the early CMOS, That is, when the current changes, the frequency becomes faster, which inevitably generates heat, which eventually causes the appearance of noise on the screen and affects the imaging quality.
If you compare CCD and CMOS sensors, the biggest advantage of CCD is that the imaging quality is high. The biggest advantage of CMOS is that it has low cost and is easy for mass production. With the disadvantages of CMOS, it is constantly being improved. .
At present, some medium format digital cameras or digital backs still use CCD sensors. This is because different products have different requirements for picture quality. Therefore, those medium format digital products are often more expensive than ordinary digital cameras.
Therefore, it can be said that the main development direction of the future camera market will still be based on CMOS, and on this basis, the resolution and sensitivity of CMOS will continue to increase.
The era is advancing, and cost saving is a business rule that every business is adhering to. The future of CCD is not necessarily in the camera market. In other areas, CCD will be widely used due to its own advantages.
As technology continues to grow, I believe that at some point in the future, there will certainly be more kinds of sensors. This is only a matter of time. Then we look back and look at the film era and CCD era we have experienced. In the era of CMOS, we will sincerely lament the rapid development of science and technology.
Comparison of CCD and CMOS
1, the imaging process
CCD and CMOS use the same photosensitive material, so the basic principle of electron generation after receiving light is the same, but the reading process is different: the CCD is transferred in frame or line mode with the synchronization signal and clock signal. The whole circuit is very complicated. The output rate is slow; CMOS reads the signal in a DRAM-like manner. The circuit is simple and the read rate is high.
2, the degree of integration
CCD readout circuits using special technologies are relatively complex, it is difficult to integrate A/D conversion, signal processing, automatic gain control, precision amplification and memory functions on a single chip. Generally, it takes 3 to 8 chip sets to realize it. A multi-channel non-standard supply voltage.
With large-scale integrated manufacturing processes, CMOS image sensors can easily integrate the above functions into a single chip. Most CMOS image sensors have both analog and digital output signals.
3, power supply, power consumption and volume
The CCD needs a variety of power supplies, consumes more power, and has a larger volume. CMOS only requires a single power supply (3V~5V), its power consumption is equivalent to 1/10 of the CCD, and highly integrated CMOS chips can be made quite small.
4, performance indicators
CCD technology is quite mature, and CMOS is in a period of vigorous development. Although high-end CMOS image quality is temporarily inferior to CCD, some indicators (such as transmission rate, etc.) have exceeded CCD. Because CMOS has many advantages, many institutions at home and abroad have applied CMOS image sensors to develop many products.
Six Hardware Specifications of CCD and CMOS Image Sensors
Sometimes people may have such a question, why is the difference in image quality of high-definition webcams? Why are the effects different at night when using the same accessories? In fact, this is related to the hardware specifications of the sensor (ie, image sensor) we use. Whether it is a CCD or a CMOS image sensor, there are mainly "pixel, target size, sensitivity, electronic shutter, frame rate, and signal to noise ratio." These six hardware technical indicators.
Pixel:
There are many light-sensing units on the sensor that convert light into electrical charge, creating an electronic image that corresponds to the scene. In the sensor, each photosensitive cell corresponds to one pixel. The more pixels, the more pixels it can sense, and the more clear the image, the higher the pixel size, which means the clearer the imaging effect.
Pixel:
Related to our products in the century: 100W network camera resolution is 1280X720, the two values ​​are multiplied by the pixel value, that is nearly 1 million pixels, 130W resolution is 1280X960, the pixel value is nearly 1.3 million Pixels. From the image effect, 130W is better than 100W.
Target size:
The size of the photosensitive part of the image sensor is generally expressed in inches. Like a television, usually this data refers to the diagonal length of the image sensor. If it is 1/3 inch, the larger the target, the better the amount of light, and the smaller the target, the easier it is to obtain. Greater depth of field.
For example, 1/2 inch can have a relatively large amount of light, and 1/4 inch can easily obtain a larger depth of field. "Associating our products from Zhongwei Century: 100W products are 1/4 inch, 130W is 1/3 inch, and 200W is 1/2.7 inch. Everyone can perceive the above-mentioned different target plane sizes from the screen. The image quality changes.
Sensitivity:
That is, the intensity of incident light is sensed by CCD or CMOS and related electronic circuits. The higher the sensitivity, the stronger the sensitivity of the light-sensitive surface, and the higher the shutter speed. This is especially important when shooting moving vehicles and monitoring at night.
This explains why night vision differs from camera to camera. The unit of sensitivity is V/LUX-SEC, V (Volt) is the unit of voltage that we usually refer to, and LUX-SEC: is the unit of weak light. The greater the ratio, the better the night vision effect.
Electronic shutter:
It is a term coined for the mechanical shutter function of the camera. It controls the sensitometric time of the image sensor. Since the sensitometric value of the image sensor is the accumulation of the signal charge, the longer the sensitometry, the longer the signal charge accumulation time and the greater the amplitude of the output signal current. The faster the electronic shutter, the lower the sensitivity, making it suitable for shooting in bright light.
Frame rate:
Both refers to the number of pictures recorded or played back in unit time. Continuously playing a series of pictures will produce animation effects. According to the human visual system, when the picture's playing speed is greater than 15 frames per second (ie, 15 frames), the human eye basically cannot see the jumping of the picture; it reaches 24 frames. /s~30 frames/s (ie, 24 frames to 30 frames) are basically not aware of flickering.
The frames per second (fps) or frame rate represents the number of times the graphics sensor can update every second while processing the field. A high frame rate gives a smoother, more realistic visual experience.
Signal to noise ratio:
It is the ratio of the signal voltage to the noise voltage. The unit of signal-to-noise ratio is expressed in dB. The signal-to-noise ratio given by the general camera is the value when the AGC (Automatic Gain Control) is turned off, because when the AGC is turned on, the small signal is boosted, so that the noise level is also increased accordingly.
The typical signal-to-noise ratio is 45-55dB. If it is 50dB, there will be a small amount of noise in the image, but the image quality is good. If it is 60dB, the image quality is good and no noise occurs. The larger the signal-to-noise ratio, the more noise is controlled. it is good. The number of noises in the image of this parameter relationship is higher, and the higher the signal-to-noise ratio, it gives the impression that the cleaner the screen is, the less the noise in the night vision screen is.
Conclusion:
At present, CCD is still superior to CMOS in terms of performance. However, with the continuous advancement of CMOS image sensor technology, based on its inherent integration, low power consumption, and low cost advantages, noise and sensitivity have greatly improved, and the gap with CCD sensors is continuously narrowing. Even some industry insiders believe that the future sensor market should be the world of CMOS. So, which sensor is more suitable for the industrial camera market? Or which sensor is more suitable for future needs?
For the above questions, the answer is obvious: There are many tradeoffs to consider when choosing a chip.
CCD and CMOS image sensors have their own advantages and disadvantages. In the entire image sensor market, they are both a competition and a complementary relationship. In some cases, the two sensors are complementary and can be used in different applications. . No matter which kind of sensors are more powerful, their technological advances will undoubtedly greatly promote the development of the image sensor market and the machine vision industry.
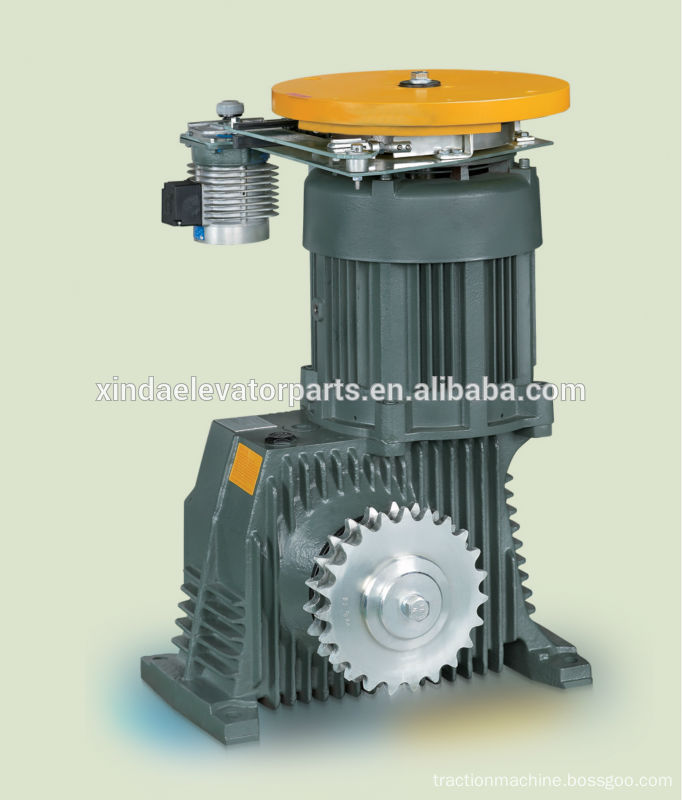
Specifications
energy-saving, less maintenance, low noise
Suit for all kinds of machine room above lift/elevator
Gearless Traction Elevator for Escalator Machine
Product Characteristics
Drive: VVVF drive
Deadweight: 320kg/430kg
Noise level:<58dB(A)
Torsional vibrations: <0.8~1.2mm/s ;<2.0mm/s
Horizontal and vertical vibrations: <0.8~1.2mm/s
Rated output torque: 886N·m~1463N·m; 1072N·m~2925N·m
Arrangement: right side